China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. This article dives into the incredible rise of China’s manufacturing sector, exploring its historical context, current dominance, and future prospects. We’ll examine the key factors behind its success, the challenges it faces, and the global implications of its manufacturing might. Get ready for a fascinating look at the engine room of the global economy.
From humble beginnings, China transformed itself into a global manufacturing giant. We’ll trace its journey, highlighting pivotal moments and analyzing the strategic decisions that propelled its growth. We’ll also delve into the specific sectors where China excels, profiling leading companies and assessing their impact on international markets. Prepare to be surprised by the sheer scale and complexity of China’s manufacturing prowess.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a huge amount of medical equipment, including surgical tools, is made there. If you’re interested in that field, you might want to check out surgical tech programs near me to learn more about the technology behind it all. Ultimately, understanding the supply chain, from China’s factories to the operating room, is key to grasping the whole picture.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance
China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing superpower is a remarkable story of economic transformation. From a largely agrarian economy, it has evolved into a global manufacturing hub, impacting global supply chains and international trade significantly. This article delves into the historical context, current state, challenges, future prospects, and global implications of China’s manufacturing prowess.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – it’s a huge global network, right? So, news like this Canadian recall of certain sea and Himalayan salts, Sea and Himalayan salts recalled in Canada: ‘Do not use, serve or , highlights how a problem anywhere can ripple through that vast system. It makes you wonder about supply chain issues and the scale of potential impacts when something goes wrong in such a massive manufacturing powerhouse.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context

China’s journey to manufacturing dominance began with gradual industrialization following the establishment of the People’s Republic in 1949. Key factors like the implementation of economic reforms in the late 1970s, the influx of foreign direct investment, and a large, relatively low-cost labor force propelled its growth. Compared to other manufacturing giants like the US and Japan, China’s trajectory was characterized by rapid expansion and a focus on export-oriented manufacturing.
| Date | Event | Impact | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | Economic Reforms (Deng Xiaoping’s reforms) | Opened China to foreign investment and market-oriented reforms, laying the foundation for manufacturing growth. | Significant increase in GDP growth rates post-1978. |
| 1980s-1990s | Establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) | Attracted foreign investment and spurred export-oriented manufacturing. | Rapid growth of export-processing industries in SEZs like Shenzhen. |
| 2001 | Accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) | Further integrated China into the global trading system, accelerating its manufacturing expansion. | Substantial increase in China’s global trade volume following WTO accession. |
| 2010s-Present | Focus on technological advancement and domestic consumption | Shift towards higher value-added manufacturing and reduced reliance on low-cost labor. | Government initiatives promoting technological innovation and industrial upgrading. |
Current State of Chinese Manufacturing
China’s manufacturing dominance is evident across numerous sectors. It is a leading producer of electronics, textiles, machinery, and consumer goods. Companies like Huawei, Foxconn, and Tencent are global players, significantly impacting their respective industries.
That Hacker News thread on China’s manufacturing dominance is fascinating! It makes you think about the global supply chains, and how a massive sporting event like a cricket match, where you can read about Rickelton’s double-century and Verreynne’s fifty propelling SA to 429 , probably relies heavily on goods manufactured in China. It’s all connected, right?
So, back to that Hacker News discussion – the scale of Chinese manufacturing is truly mind-blowing.
| Sector | Output Value (USD Billion) (Illustrative) | Global Market Share (Illustrative) | Key Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | 1500 | 40% | Smartphones, computers, consumer electronics |
| Textiles | 500 | 30% | Clothing, fabrics, yarn |
| Machinery | 800 | 25% | Industrial machinery, construction equipment |
| Consumer Goods | 1200 | 35% | Toys, furniture, household appliances |
Manufacturing is geographically concentrated in coastal provinces like Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang, but is increasingly diversifying to inland regions.
Challenges and Future Prospects of Chinese Manufacturing, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
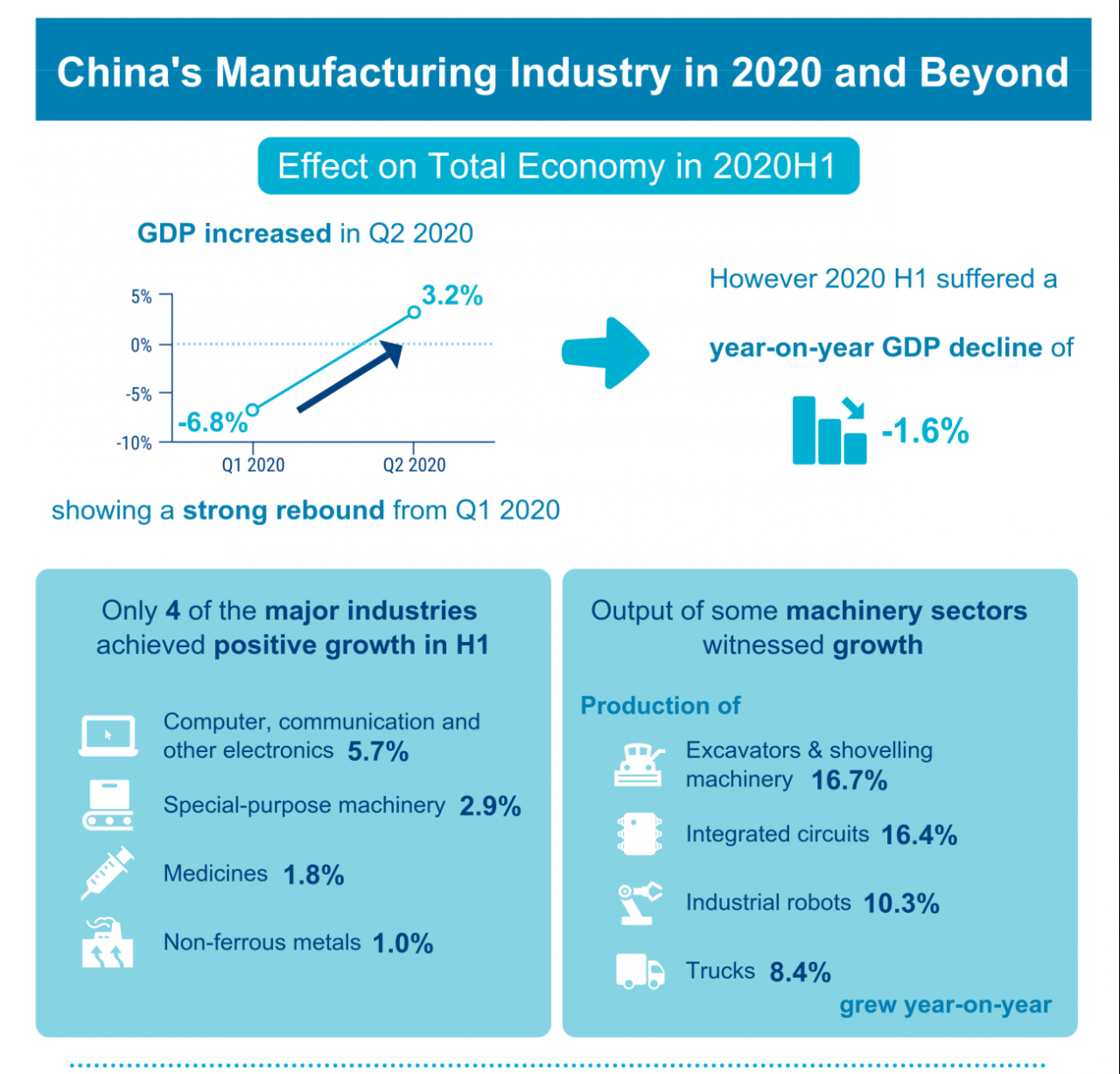
China’s manufacturing sector faces challenges such as rising labor costs, environmental regulations, and the need to upgrade technologically. Automation and AI are transforming the sector, impacting employment and productivity. To maintain its leadership, China is investing heavily in technological innovation and promoting industrial upgrading.
- Increased automation and AI adoption will lead to higher efficiency and productivity but also potential job displacement in low-skill sectors.
- China will focus on higher value-added manufacturing, moving away from labor-intensive industries.
- Environmental concerns will drive the adoption of greener manufacturing practices and sustainable technologies.
- China’s manufacturing sector will experience continued growth, but at a slower pace compared to the past, driven by domestic consumption and technological advancements.
Global Implications of China’s Manufacturing Power

China’s manufacturing dominance profoundly affects global supply chains, trade balances, and international relations. Many countries heavily rely on China for manufactured goods. A significant reduction in China’s manufacturing output would cause major disruptions to global markets.
The dependence on Chinese manufacturing is a double-edged sword. While it offers cost advantages, it also creates vulnerabilities for countries heavily reliant on Chinese production.
Economist Perspective
A decline in Chinese manufacturing could lead to shortages, price increases, and disruptions in global supply chains, impacting businesses and consumers worldwide.
Business Perspective
Geopolitical implications are significant. A shift in manufacturing away from China could reshape global power dynamics and trade relationships.
Geopolitical Analyst Perspective
Technological Innovation in Chinese Manufacturing
China is making significant strides in robotics, automation, and 5G technology within its manufacturing sector. While still catching up to some Western nations in certain areas, China’s pace of innovation is rapid, driven by government support and investment. Technological advancements are shaping the future of Chinese manufacturing by improving efficiency, productivity, and quality.
For example, consider a hypothetical innovative manufacturing process using AI-powered predictive maintenance. Sensors embedded in machinery constantly monitor its performance, predicting potential failures before they occur. This allows for proactive maintenance, minimizing downtime and optimizing production schedules. This system, coupled with advanced robotics for assembly and quality control, drastically increases efficiency and reduces waste.
End of Discussion

China’s manufacturing dominance is a multifaceted story of remarkable growth, strategic planning, and ongoing challenges. While its future isn’t without hurdles – rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and technological disruption being key among them – China’s proactive approach to innovation and adaptation suggests a continued significant role in global manufacturing for years to come. Understanding this powerhouse is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern global economy.
User Queries: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
What are some of the ethical concerns surrounding Chinese manufacturing?
Concerns include labor practices, environmental impact, and intellectual property rights. These are complex issues with varying perspectives and ongoing debates.
How does China’s manufacturing sector compare to that of the US?
While the US retains strengths in specific high-tech sectors, China significantly surpasses the US in overall manufacturing output and global market share across many industries.
What are the risks associated with over-reliance on Chinese manufacturing?
Risks include supply chain vulnerabilities, geopolitical tensions, and potential disruptions to global markets if unforeseen circumstances impact Chinese production.
